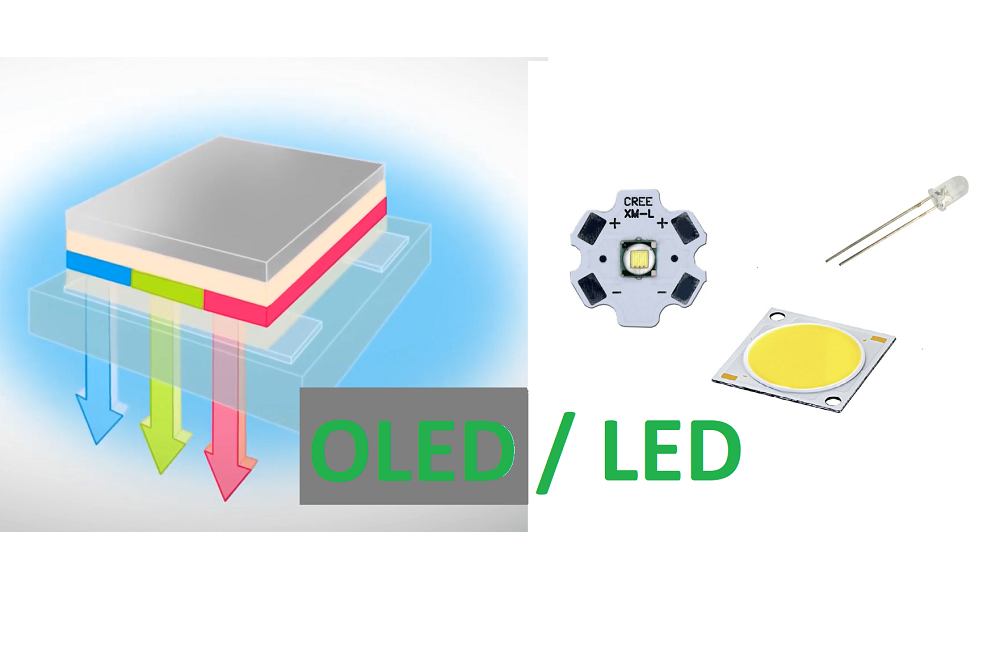
Lighting technology has evolved considerably in recent decades, and there is now a wide variety of light sources. LED (Light Emitting Diode) and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) lighting are two technological innovations that have gained great popularity thanks to their energy efficiency, environmental friendliness and versatility.
OLED and LED
However, there are differences in structure, function and characteristics between the two technologies, which makes for an interesting comparison.
LED technology uses semiconductors to move electrons from a lower energy level to a higher energy level as they emit radiant energy as light.
OLED technology, on the other hand, relies on organic molecules to pass an electric current through them, creating photons, or light.
To better understand the differences, this article will look at LED and OLED lighting from several perspectives: from materials and components to effects, applications and economics.
The aim is to provide an in-depth analysis and evaluation of the relative advantages and disadvantages of each technology to help readers make informed decisions about their lighting solutions.
Scientific background of OLED and LED technology
Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) technology offers many advantages, including a slim form factor, wide viewing angle (TV), low power consumption and excellent colour accuracy.
LED technology, on the other hand, has the disadvantage of less vivid and accurate colours (TV) and higher power consumption.
What is the difference between OLED and LED lighting from a manufacturing process perspective?
OLED manufacturing and LED production differ in many ways, including the materials used, production costs and manufacturing challenges.
OLED technology is based on organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through them, while LEDs use semiconductors such as gallium nitride or indium gallium nitride.
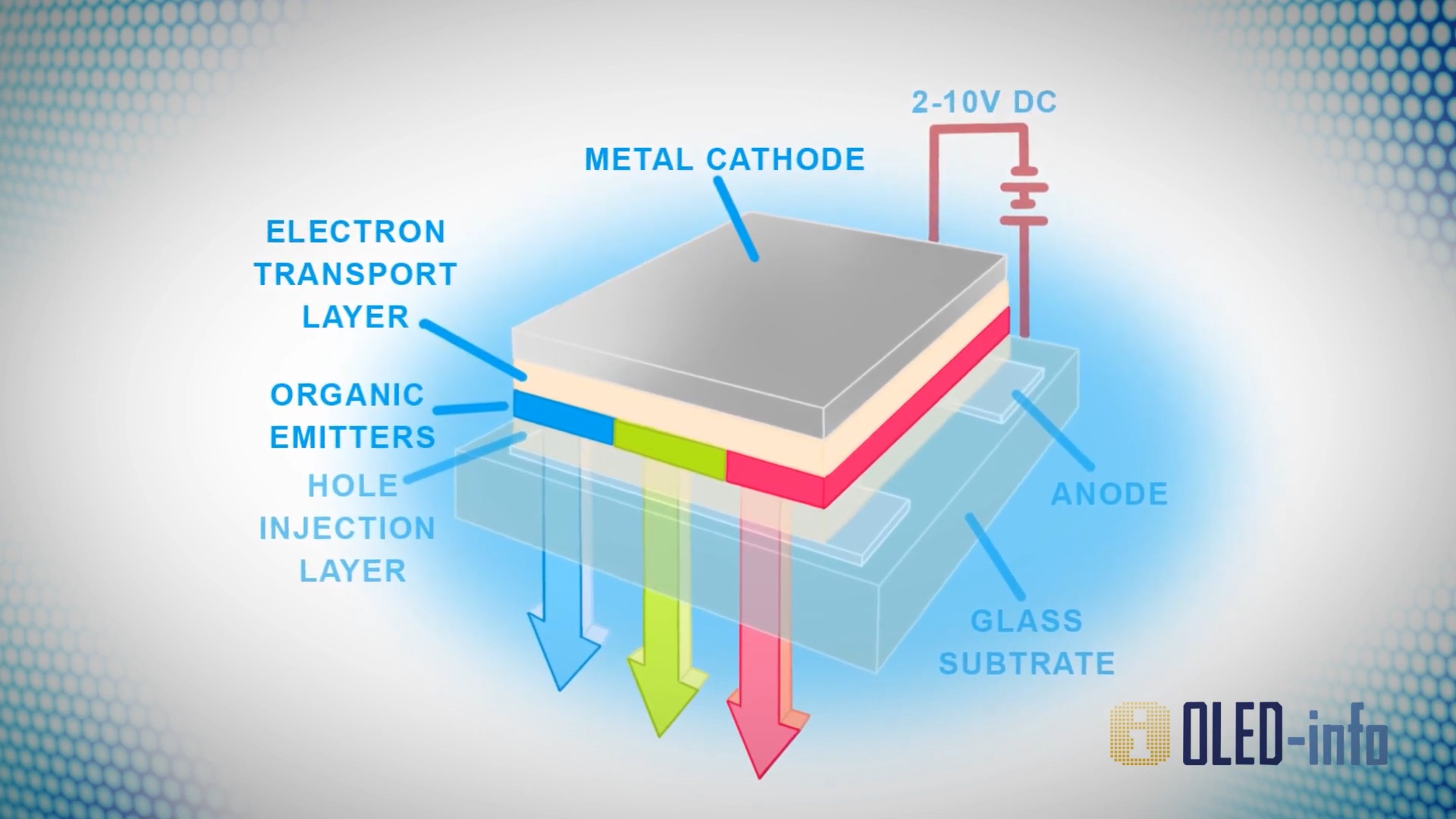
Due to the different materials, the manufacturing processes are also different: for growing thin films for OLED components, evaporation techniques such as thermal evaporation or plasma-assisted chemical vapour deposition (PE-CVD) are typically used, while for LEDs, higher temperature epitaxial processes are required.
OLEDs have the advantage that they can be produced on flexible substrates, enabling the development of new types of applications such as foldable displays and smart clothing.
On the other hand, this technology faces the challenge of greater sensitivity to humidity and oxygen in the air and a shorter lifetime compared to LEDs. OLED manufacturing costs are also generally higher than for LEDs, due to factors such as the special materials and process equipment required.
As a result, there is still much to be developed in the market, both in terms of technology and production processes, before OLEDs can compete more widely with LEDs.
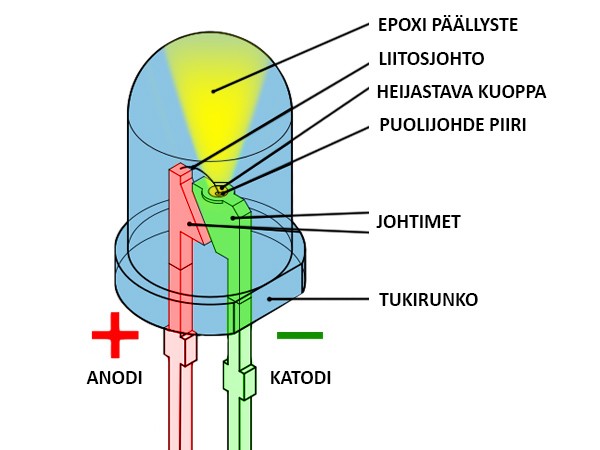
The advantages of OLED
Although OLED and LED technologies are both lighting solutions, OLED lighting has significant advantages over traditional LEDs.
Firstly, organic materials allow thinner and lighter panels to be produced, leading to significantly improved energy efficiency. This will also reduce the cost of maintaining the equipment.
In addition, the flexibility of OLED lights makes them ideal for flexible applications such as displays integrated into smartphones, computers or even clothing, and in the future also for lighting.
Overheating is a concern for many LED products: higher temperatures can shorten the lifetime of devices and require more efficient cooling technology, which increases costs and energy consumption. Of course, in this case, the energy consumption for conventional lighting sources, for example, is huge for both technologies. OLED technology produces less heat than traditional LED technology (35 vs 70 degrees)
Overall, OLED technology represents a significant step forward for the lighting industry thanks to its many benefits for both consumers and professionals.
Disadvantages of OLEDs
LED technology has been dominating the lighting market for years, it also has advantages over the newer upcoming OLEDs.
The most significant of these is the LED lifetime of +50,000 hours, while OLED lifetime is “only” 10-50,000 hours depending on the luminaire. In addition, OLED technology has a particularly troublesome catch-up, or “memory”, feature of OLED circuits.
In addition, traditional LED technology gives more light per watt, meaning it is even more efficient.
OLED efficiency is currently max. 60 lumens per watt, while a conventional LED already produces 140 lumens per watt when the full light spectrum option is taken from both. New products including OLED on the website
Identifying these challenges will help to develop better lighting solutions for the future and direct designers’ attention to the opportunities offered by organic materials, such as OLED technology.
Comparison of energy efficiency
When comparing the energy consumption of LED and LED lighting, both energy savings and costs need to be taken into account.
Both technologies have the potential to save energy, but due to some of the more cost-effective features of oled lighting, it is the more economically preferable option.
Energy saving
Energy savings are an important factor when comparing lighting technologies, as they affect not only energy consumption and costs, but also the environmental impact.
OLEDs and lights differ in efficiency due to differences in design and materials.
Smart homes technology allows for more innovative use of these lighting solutions, which can lead to significant savings in energy consumption.
For example, timers, motion or occupancy sensors and remote management features can optimise lighting according to need, minimising the necessary energy waste.
While OLED technology offers thinner and more flexible panels compared to LED luminaires, the latter often have a better efficiency, i.e. they produce more light for the energy they consume.
This suggests that both technologies have their own advantages for different applications, but LED luminaires may still be preferable where energy efficiency is critical.
Cost comparison
Cost comparison is another important aspect of assessing the energy efficiency of lighting technologies.
Taking into account the initial investment and maintenance costs helps to achieve a comprehensive understanding of the overall cost-effectiveness of both technologies.
Although OLEDs may be thinner and more flexible, they have a higher purchase price than lights, which affects the initial investment.
On the one hand, the higher efficiency of lights luminaires generally means lower energy costs in the long term, but the associated maintenance costs also have to be taken into account for different applications.
A simple example of this is LED lamps, which offer a longer life than incandescent lamps, reducing the labour and material costs associated with lamp replacement.
It is therefore important to assess both the initial investment and the potential maintenance and energy saving costs before making a final decision on the best lighting solution for a particular site or situation.
Lifespan and Sustainability
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) technology is known for its longer lifetime, and in some cases is estimated to last up to 10 years of continuous use (100,000 hours) BUT there is a big BUT.
OLED technology can achieve a long lifetime ONLY if it is used at low power, i.e. only approx. 20 lumens per watt.
LED lighting, on the other hand, generally has a lifetime of around 50 000 hours, depending on the type and quality of the product when the LED circuit is used at its recommended power.
The table below shows the lifetime of different technologies at different power levels. By default, the cooling is done correctly:
| Type of light | 10 lm/W | 25 lm/W | 50 lm/W | 75 lm/W | 100 lm/W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LED light | Approximately 150 000 hours | Approximately 100 000 hours | Approximately 80 000 hours | Approximately 60 000 hours | Approximately 50 000 hours |
| OLED light | Approximately 200 000 hours | Approximately 100 000 hours | Approximately 30 000 hours | Approximately 20 000 hours | Approximately 10 000 hours |
LED lighting is also more reliable and stable than OLED, making it a better choice for many applications.
The durability of Oled technology
While the longevity and durability of OLED lighting have improved significantly in recent years, it is important to understand that they are not yet fully equivalent to LED lighting.
A key reason for this is the occurrence of OLED degradation factors over time: as organic materials react with light, their stability gradually deteriorates, affecting product performance and lifetime.
As a result, OLED solutions may lose brightness faster than competing LED technologies.
While research continues to address these challenges, it is clear that improving the stability of organic materials remains an obstacle to the wider application and market growth of OLED lighting.
Led service life
Moving on to the lifetime of LED lighting, it should be noted that it offers several advantages over OLED technology.
One key difference concerns degradation: unlike organic materials, LED components do not degrade as quickly when exposed to light.
As a result, their performance and lifetime are longer than OLED solutions.
In addition, LED lighting systems have lower maintenance requirements, making them more cost-effective in the long term and easier to install and maintain in a variety of applications.
However, it is worth remembering that LED technology also has its own challenges, including thermal management and cooling solutions, which can affect the reliability and durability of products.
LED reliability
Moving on to the reliability of LED lighting, it should be noted that these luminaires are generally robust and durable.
In addition, they often require less maintenance than OLED solutions, making LED technology a more cost-effective option, especially in the long term.
By combining LED lighting with the integration of intelligent control, greater energy efficiency can be achieved and the lifetime of light optimised without the need for ongoing or complex maintenance.
However, thermal management and cooling solutions are key to ensuring optimal performance and reliability in a wide range of applications and conditions.
Colour reproduction and brightness
When it comes to OLED and LED lighting, colour accuracy, brightness and tone are important factors.
In general, OLED lighting offers better colour accuracy and brightness, while LED lighting tones are often less accurate.
In addition, the brightness of LED lighting can vary greatly, as there are many different manufacturers of luminaires on the market.
In terms of colour tones, LED lighting often offers a wide range of different shades, whereas OLED lighting is rather limited.
Colour accuracy
Colour accuracy is an essential factor in lighting, affecting how well objects are seen and how colours are reproduced under a light source.
There are differences between OLED and LED lighting in the way colours are managed.
Colour control or temperature control (CCT) refers to the ability to continuously adjust the ratio of different colour spectra within the same light source. And how pleasantly the eyes perceive colours in different lighting situations.
In general, OLED technology offers better colour accuracy compared to traditional LEDs, because its thin organic layers can produce a wider colour gamut and more subtle colour nuances in a more natural way.
This makes skin tones, for example, look more realistic and balanced under OLED lighting when compared to low-cost LED lighting.
Brightness levels
Controlling the brightness levels of lighting is another key aspect, alongside colour calibration and tone control.
Brightness affects how well objects stand out under light.
Differences between OLEDs and lights can be observed in this respect.
One major advantage of OLED technology is its greater brightness control compared to traditional LEDs.
This allows OLED luminaires to provide effective glare control and soft shadows without the visual distraction of high contrasts. The OLED light panel can even be used to turn off individual pixels of light.
In addition, the wide dynamic range allows for more subtle details to be highlighted and more vivid colours to be seen even in low light or at longer viewing distances, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.
Colour temperature
Colour temperature is also an essential part of colour and brightness management in lighting, as it directly affects the perception of colours in different lighting situations.
Colour temperature control can significantly improve colour perception and visual comfort, as well as adding to the aesthetics and functionality of spaces.
The differences between OLEDs and lights can be seen not only in their ability to provide a wide dynamic range and better contrast, but also in their colour temperature control.
OLEDs generally offer more efficient thermal regulation than traditional LEDs, allowing for more subtle colour transitions while preventing excessive heat build-up or reduced energy efficiency.
As a result, OLED luminaires, which are more versatile in terms of their applications, are able to respond to more accurate colour management and optimal conditions to perform critical tasks or create a pleasant atmosphere in the interior of different spaces.
Design flexibility and versatility
OLED lighting offers many design possibilities, including a slim profile, low heat output and simple installation.
The use of LED lighting allows for versatile design and easy installation.
LED lighting is also more adaptable, as it can be customised to suit your needs.
Design options
Both lighting technologies, OLED and LED, offer a range of design options that allow for innovative aesthetics and adaptable shapes.
OLED technology offers a thinner and more flexible structure compared to traditional LEDs, opening up new possibilities in lighting design for vehicles or architectural applications.
On the other hand, LEDs are still well established in the market thanks to their energy efficiency and long lifetime.
They can be combined in a variety of configurations such as strips, panels or even more complex structures to respond to the requirements and visual appearance of the space.
Thus, by exploring both OLED and LED technologies, the most suitable solutions for different project needs can be found.
Types of installation
The diversity and flexibility of lighting design is also reflected in the different types of installation that both technologies allow.
OLED and LED lights can be used in a wide range of applications, from small detailed lights to large-scale luminaires, and can be intelligently integrated with different surfaces or structures.
Installation challenges can vary depending on the characteristics and requirements of the solutions chosen and their location in the space.
For example, flexible OLED panels can be used to create curved shapes without additional structures, while LEDs are better suited for linear applications or places where more power is needed while the size of the light source is compact.
Intelligent integration allows lighting solutions to be integrated into an automated system, making adjustments easy and adaptable for the end user.
As a result, comparing different types of installation will help you find the best solution for your needs, taking into account both aesthetic and functional aspects.
Customization options
In lighting design, individuality and a personalised atmosphere are important factors that influence the look and feel of a space and the comfort of its users.
The versatility offered by OLED and LED lights allows a wide range of customisation options to create the lighting ambience you want.
In addition, intelligent integration allows seamless control of different light sources from a single location or according to automated scenarios.
For example, the adjustment of colour tones, brightness and light direction is easy for both professionals and end-users, contributing towards a perfectly adapted lighting solution.
Environmental impact and sustainable development
OLED and LED lighting are both energy-efficient alternatives compared to traditional light bulbs.
LED light sources have lower CO2 emissions than OLED light sources, but OLED light sources offer better energy efficiency.
OLED and LED light sources are both recyclable and reusable in Finland.
Energy efficiency
From an energy efficiency perspective, there are significant differences between OLED and LED lighting technologies. However, energy-saving tips can optimise the energy consumption of both types of luminaires and reduce their environmental impact.
In general, LED lights are known for their better energy efficiency compared to OLED technology, but innovative applications can improve the performance of the latter in certain situations.
In the future, experts in the field will seek to find solutions through further technological advances to make it easier to meet environmental challenges.
Carbon footprint
In terms of carbon footprint, there are important differences between OLED and LED lighting technologies that affect the environmental impact of these luminaire types.
To reduce carbon emissions, new eco-innovations are constantly being developed to help improve the energy efficiency of both technologies and thus reduce their carbon footprint.
For example, the thinner structure allows OLED panels to be used with complex shapes, which can lead to more efficient use of materials and a smaller carbon footprint.
Further research will focus on finding more efficient solutions for both OLED and LED technologies to meet the growing environmental challenges now and in the future.
Recycling & Reuse
From an environmental and sustainability perspective, the comparison of the recycling and reuse potential of OLED and LED lighting is also important.
Recycling problems are common to both technologies, as they involve complex materials and components that require special handling methods for disposal.
However, innovative reallocation offers the opportunity to improve the life cycle of both lighting technologies and reduce their environmental impact.
For example, the phosphor layer of discarded LED lights can be used to make other products, or the organic materials of old OLED panels can be explored for new applications such as biodegradable electronics.
Such an approach, while requiring more efficient recycling processes and infrastructures, can increase the long-term environmental sustainability of these technologies.
Cost analysis and total value
A price comparison between oled and LED lighting can be considered in terms of both cost and productivity.
The evaluation shows that oled lighting offers better performance and durability at a lower price than LED lighting.
Cost comparison
While the purchase costs of OLED and LED lighting can vary considerably, it is important to consider other cost factors when assessing their overall value.
For example, the complexity and time of the installation process can have a significant impact on the labour and material costs associated with the project and the lifetime of the lights.
OLED lights can be thinner and more flexible than traditional LEDs, making them an attractive alternative for certain applications.
On the other hand, LED products are generally more durable and can offer better energy efficiency compared to LED products while having less heat loss.
Maintenance requirements also play a major role in the cost analysis: while both types of light are known for their long lifetime – in some cases up to 50 000 hours or more – the perhaps longer lifetime of LEDs can offer savings in terms of replacement costs, especially in situations where access to luminaires is difficult or particularly expensive.
Despite the fact that the differences between the two lighting technologies may seem insignificant at first glance, looking at the overall value can help determine the best solution for different needs and budget constraints.
Value comparison
When evaluating the cost analysis and overall value, it is important to make a value-based comparison between OLED and LED lighting. This includes considering light features such as OLED longevity and a more versatile range of applications, as well as LED applications that offer improved energy efficiency and durability.
The objective and person-centred approach of academic studies helps to identify the strengths and weaknesses of both technologies in different situations. This allows the best choice to be determined, taking into account their economic impact, performance, environmental and social consequences.
While each case has its own unique circumstances, this type of analysis can provide a deeper understanding of which solutions are best suited to specific areas or projects without placing undue strain on budgets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there certain applications or industries where OLED or LED lighting is more suitable or preferable to one or the other?
For different applications and industries, the suitability or popularity of OLED and LED lighting varies.
The flexibility of OLEDs allows them to be used in curved and flexible light sources, which can be useful for architectural design, for example.
On the other hand, the efficiency of LEDs makes them an excellent alternative for energy-efficient lighting, such as street lights or indoor lighting for businesses.
When comparing colour reproduction, both have their advantages: OLEDs offer a smoother colour dispersion, while LEDs can achieve a higher colour rendering index (CRI).
Both OLED and LED have evolved in the field of smart lighting solutions, but in general, smarter homes and public spaces tend to use more LED-based solutions due to their better energy efficiency.
Sustainability impacts are also important factors when deciding between the two; although the life cycle of both technologies has lengthened in recent years, the longer life of LED lamps tends to give them a slight ecological advantage.
How do OLED and LED lighting technologies perform in extreme temperatures or outdoor conditions?
Comparing the performance of OLED and LED lighting technologies in extreme temperatures or outdoor environments involves a number of factors such as extreme temperature performance, outdoor lighting performance, weather resistance comparison and suitability for demanding applications.
Temperature effects on the life cycle of lights can be significant for both technologies. In general, LED luminaires are superior to OLEDs in many of these areas due to their excellent energy efficiency and advanced components that make them suitable for even the most challenging conditions.
In addition, LED lighting is known for its superior weather resistance compared to OLED technology, making it more attractive for outdoor furniture and other harsh applications.
While OLED technology offers improved colour rendering and a thinner structure than LED devices, it still falls short when it comes to creating an intelligent lighting solution for your difficult-to-manage environment.
Are there any health or safety risks associated with the use of OLED or LED lighting, such as possible eye strain or exposure to blue light?
The effects of blue-white light, prevention of eye strain and healthier lighting options are important considerations when buying new lighting.
Oled and LED lighting both have their advantages in these respects.
Led lights can produce higher levels of blue light, which can affect people’s sleep patterns and increase eye strain in the long term.
On the other hand, oled lights offer a more even colour temperature and reduce the proportion of blue light – this often makes them a better option for those who suffer from light sensitivity or want to minimise the potential adverse effects on falling asleep.
When choosing safe and efficient lighting solutions, it is therefore worthwhile to familiarise yourself with the characteristics of both technologies and your own individual needs by comparing research from different sources before making a decision.
Can OLED and LED lighting technologies be easily integrated into existing lighting systems, or do they require special installation methods or equipment?
The integration of OLED and LED lighting technologies into existing lighting systems is generally straightforward and does not require special installation methods or equipment.
The flexibility of lights luminaires allows them to be easily adapted to different lighting solutions while offering better colour rendering compared to conventional lighting.
LED lights are renowned for their efficiency and durability, making them a very suitable replacement for older and less energy-efficient light bulbs.
However, it should be noted that the longevity of both OLED and LED lights can vary between products due to the quality of materials and technologies used; it is therefore important to carry out appropriate research before making an investment decision.
Summary:
OLED and LED lighting technologies offer different advantages and challenges in terms of their manufacturing processes, application space constraints and performance.
On the one hand, OLED lighting offers a thinner structure and seamless light distribution, while LED technology is known for its energy efficiency and long lifetime.
When choosing the appropriate technology, it is important to take into account environmental requirements, such as temperature conditions or outdoor use, as well as potential health and safety risks.
In addition, integration into existing systems may require specific installation procedures or equipment depending on whether OLED or LED lighting solutions are chosen.
Led lighting specialist
LedStore has been an expert in led lighting since 2010. We have our own product design, so our products are technologically state-of-the-art.
We focus on light colour temperature controlled and high colour rendering index lights. We do around 500 lighting designs in a year.
We offer a service of custom-made led strips, i.e. made-to-order, easy to install led strips in profiles for everyone. Also installed.
Remember that we are always ready to offer our help to you along the way, by email (myynti@ledstore.fi) and by phone (045 251 4510). As always, feel free to share photos of your own projects on social media at ledstore.fi at Instagram and ledstore.fi at Meta. We love to see the cool things done by our LEDs, and it also helps to provide inspiration for those who are not sure about the power and awesomeness of LEDs. Did you know that we already have over 3500 pictures of our LED installations in our Gallery!
Gallery of Led lights:
Product gallery: Pictures of products in different installation locations
Indirect light: Indirect light in different spaces
Room-specific: Light in different rooms
References: Complete houses that have been photographed